Comparative Analytic of Viscoelasticity Carbon, Glass, and Graphite Fiber Composite Using Maxwell Model
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.19184/cerimre.v1i1.19545Abstract
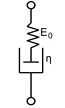
The fulfillment of the need for materials with viscoelastic characteristics to be a supporting factor. The aim is to obtain composite materials with good viscoelasticity. Vinylester matrix composite materials with variations of graphite, glass, and carbon fibers were tested using FEA and Maxwell model. The simulated viscoelasticity of the isotropic, transverse, and mixed state of glass, carbon, and graphite fibers depends on the magnitude of modulus Young and Poisson's ratio. The most significant sequence value of viscoelasticity is in graphite fiber 10,4 GPa, carbon 5,5 GPa fiber, and glass fiber 3,78 GPa.